What Is a Straight in Poker and How Do I Play It to Win?
A thorough description of a straight and its place on the poker hand rankings may be found in this poker guide. Get profitable by learning how to make and play a straight.
A straight in poker is made up of at least five unsuited cards stacked consecutively, such 4-5-6-7-8. This poker hand is characterized by either low (10-A) or high (A5) aces. A rare and coveted straight flush is indicated by suited consecutive cards. At the poker table, a straight is like a silent killer; it may appear out of nowhere and alter the course of the game.
However, a straight can become vulnerable and less dangerous if a player doesn't take advantage of its strength. Poker rules state that the player with the most number of straights wins if a game yields two. For example, KQJT9 is surpassed by AKQJT10 (Broadway) down to 5432A (wheel or bicycle). In the meantime, if two straights (AKQJT vs. AKQJT) with the same value come out of play, the pot is shared.
Categories by Hand Ranking
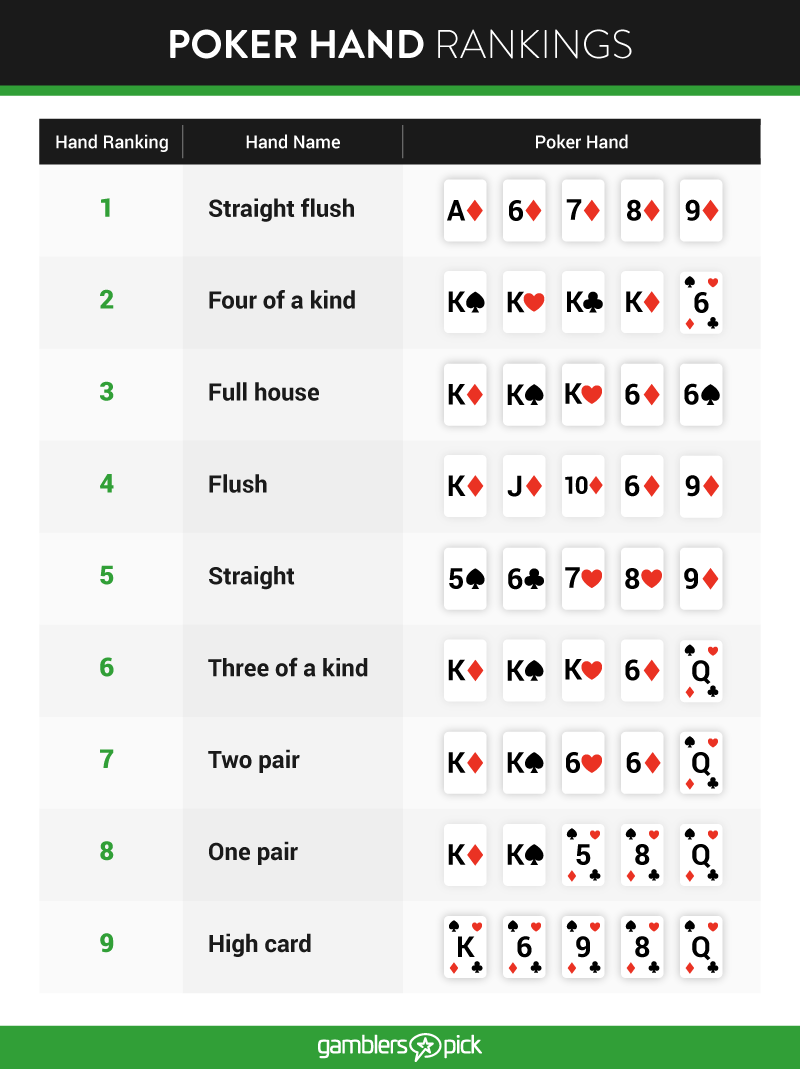
Poker hands can be compared to other hands using their ranks. The pot winner holds the lowest-ranking hands in low games like razz. On the other hand, in high games such as Texas Hold 'em and seven-card stud, the highest-ranking hands win. A hand's category is determined by the patterns the cards produce.
The position of a hand in its category is determined by the ranks of the cards. There are nine different types of poker hands, and they are ranked as follows:
- Straight flush
- Four of a kind
- Full house
- Flush
- Straight
- Three of a kind
- Two pair
- One pair
- High card
Straight Hand Rank
The denomination or hand rank is the most important factor when grading straights. When it comes to the ranking, suits are secondary. There are around 10,000 different straight hand combinations with a 52-card deck. Additionally, the deck has ten straights ranks, with the highest card descending down to determine the rank.
Similarly, superior straights are determined by the highest straight card. This factor is unaffected by the suit; a queen-high straight defeats a jack-high straight. As a result, the rank of straights that differ by suit is the same.
When two straights are on the table, who wins?
When two straights are produced in a game, there are three possible combinations that can be used to determine the winner. The winner is the player with the most valuable cards. Alternatively, if both straights produce a card with the same value, the hand becomes a tie, or a straight ending the card takes the profit. The latter starts with a rake deduction from the pot and ends with a split pot.
Players only receive a straight 0.4% of the time, so the odds of hitting one are slim. Players should concentrate on the appropriate hands to improve their chances of hitting a straight. A useful strategy to increase the likelihood of a straight is to play connected cards and one gapper. If a player discovers suited hole cards, which could result in a flush, the odds get much better. A higher straight is produced by higher cards.
The dealer may serve a straight on the table in certain games. These situations could consist of:
- AKQJT emerges from the board
- AKQJT is dealt on the table
- The table produces a lower straight than the nut straight
- A2345 (the wheel) straight is dealt on the board
The player holding the flush wins the hand if the action causes a flush on the AKQJT board. When the nut straight is on the board and there is no flush, the pot splits. Since no superior hand is attainable, every player who takes part in the showdown finishes the game with a nut straight.
When the table has a lower straight than the nut straight, players should be cautious about encountering any action. A superior straight to the one on the board can be produced by an opponent brandishing a QJ or J. If one of the opponent's hole cards has a rank greater than the top card on the board, the opponent wins. For instance, the board may feature 6789T, and one of the players holds a QJ or J.
Creating and Using a Straight to Win Strategy
Players can increase their profits more easily with a well-played straight. Although players sometimes draw two or three flops before making a straight, they do occasionally flop a straight. Open-ended draws, which allow players to deliver a gutshot (four outs) or finish of the straight (eight outs), should be the main focus.
With this result, the player has only one chance to make a hand. When the player has a 9-10 on a 6-7-J board, they need an 8. Compared to a gutshot, the odds of hitting an open-ended straight are higher in poker.
Straight Outs - Consider the advantages of hitting one of the straight outs in order to increase your chances of winning. The existence of a flush on the board determines the best option. Discounting the straight outs becomes crucial if a flush is available and there's a chance an opponent is striving for it. When holding 9d-10s on an 8h-9h-Kc board, caution is required. Because they can finish both the holder's straight and an opponent's flush draw, 7h and Qh should be avoided by players. Every out in this game counts as a half-out. As a result, the poker strategy must be modified appropriately.
Playing Draws - Choosing to draw a poker hand more quickly or more slowly might have an impact at the table. Straight draws, which call for a methodical approach, are very different from nut flush draws. A shove can result in up to 15 outs, and nut draws are often more common than straights. Straight draws, on the other hand, have weaker hole cards. A player with a straight draw is the last to act in a deep-stacked game. There may be a free card, but in order to match the chances of winning, the pot size must be restricted.
Analyzing Hands - Following a poker session, players should thoroughly examine the play to increase their chances of winning with a straight. This enables a person to adapt after encountering challenging circumstances at the table. Proficient players improve the efficacy of their poker strategy by removing errors.
Monster Flops - A player has an advantage over an opponent holding A-K when they have a pair and an open-ended straight draw on a 6-7-9 rainbow flop. Even when facing pocket aces, the advantage is clear. It enables one to challenge opponents with aggressive plays and call a raise at late position. This situation is an illustration of a monster flop that may be played slowly or quickly.
Idiot End of the Straight - People frequently assume that a straight is a winning hand when there isn't a full house or flush on the board. On a 2h-3s-9s-10d-Jc board, a player holding 7c-8c has the drawback of having the lowest straight. In poker parlance, this hand is known as the "idiot end of the straight." To prevent a catastrophic scenario, it is essential to make a well-considered move if your opponent has a K-Q or Q-8. When other players haven't shown strength, value betting is a good choice. But raising or snap calling a huge river bet necessitates a careful examination of the hand's many phases.
Concluding Remarks on Managing Poker Straights
It takes time and expertise to fully comprehend intricate poker decisions. Beginners can eventually enhance their profits by utilizing straights. In order to accomplish this goal, novice players need develop their ability to judge a hand's strength. The strength or weakness of a given card combination depends on a number of factors.
There is a crucial connection between a poker hand's strength and the number of players. Strong hands are more likely to be held when multiple players voluntarily play for the same hand. One powerful hand that is challenging for opponents to fold is a straight. In order to increase their win rate, poker players constantly want to play hands with more connections.






